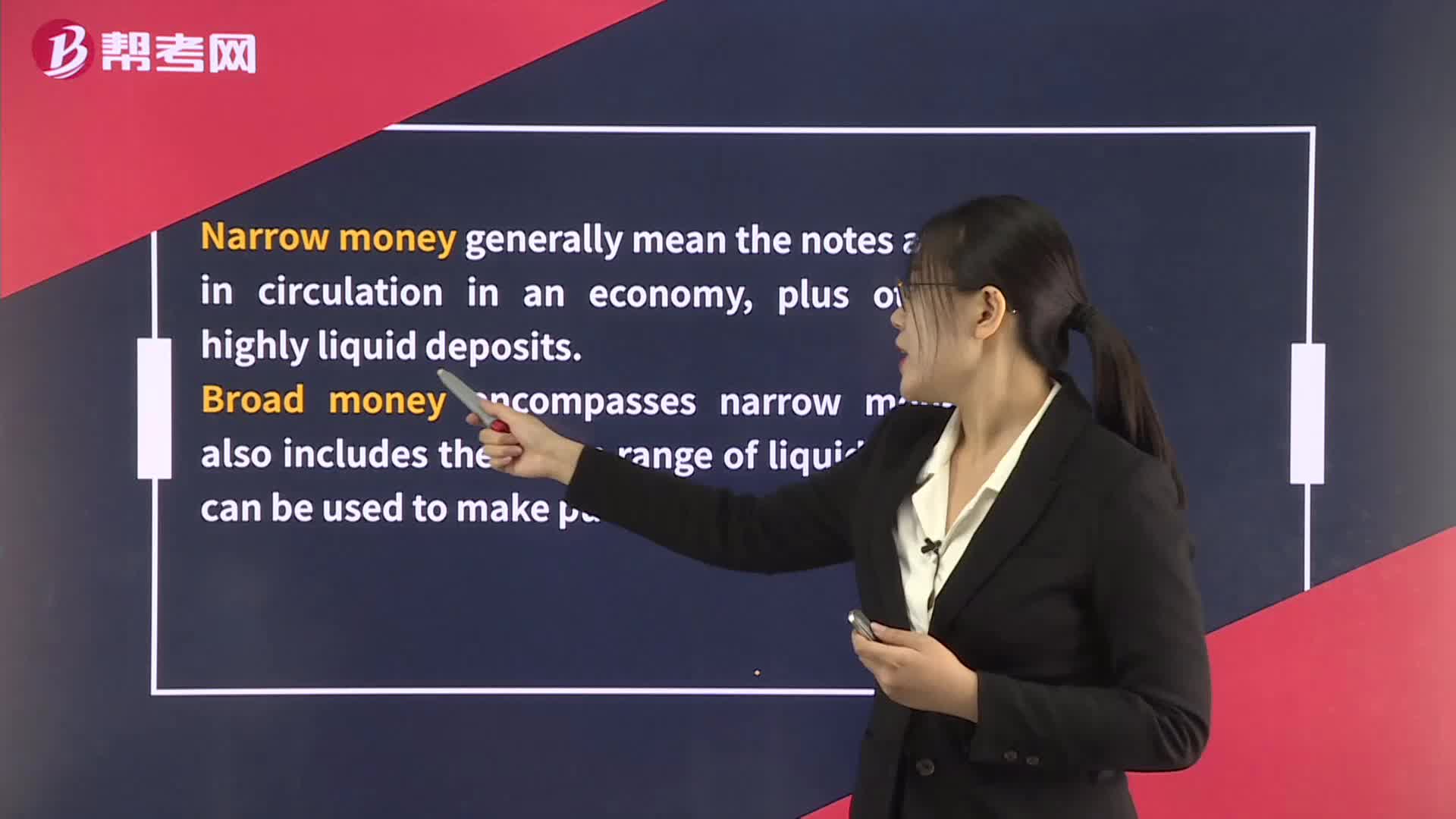
Limitations of Monetary Policy

Calculation of GDP – Expenditure Approach

Analysis of Market Structure

Monetary and Fiscal Policy

Theories of the Business Cycle - Neoclassical and Austrian Schools

Fiscal Policy

Theories of the Business Cycle - Monetarist School

Theories of the Business Cycle - Keynesian School

Fiscal Policy Tools

Fiscal Policy and Aggregate Demand

Phases Of the Business Cycle

Measures of Central Tendency

下載億題庫(kù)APP
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360