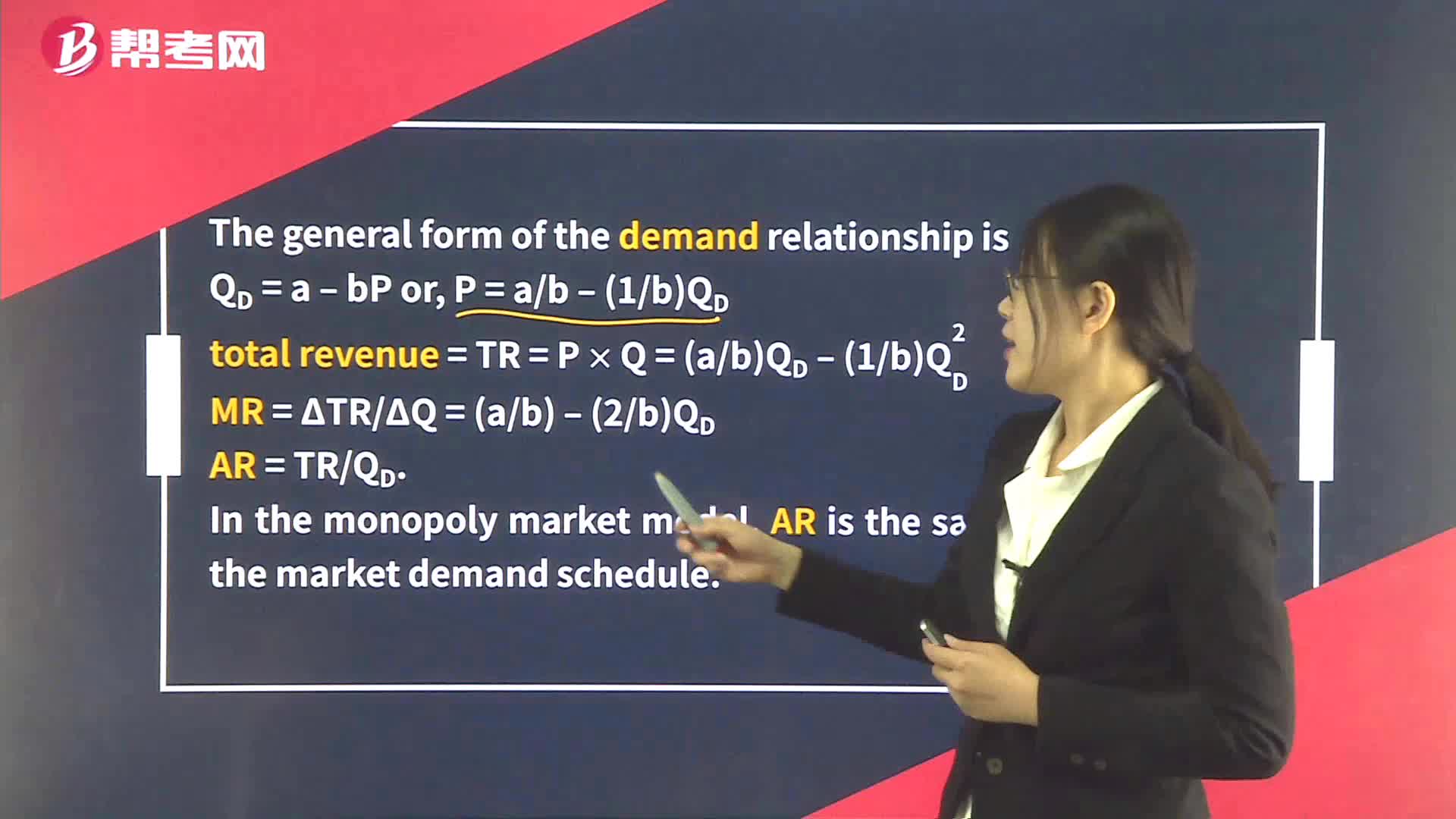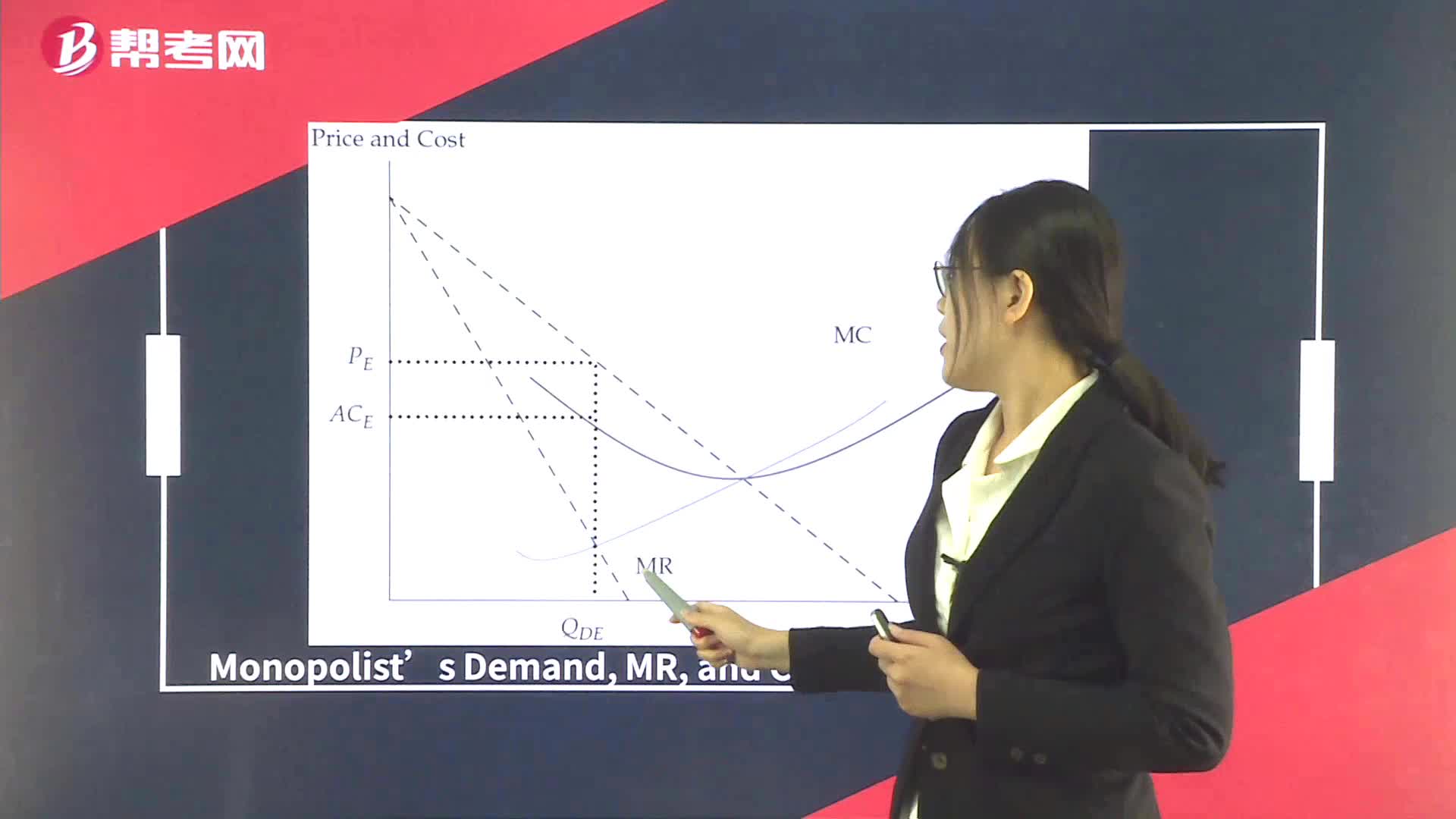
Supply Analysis in Monopoly
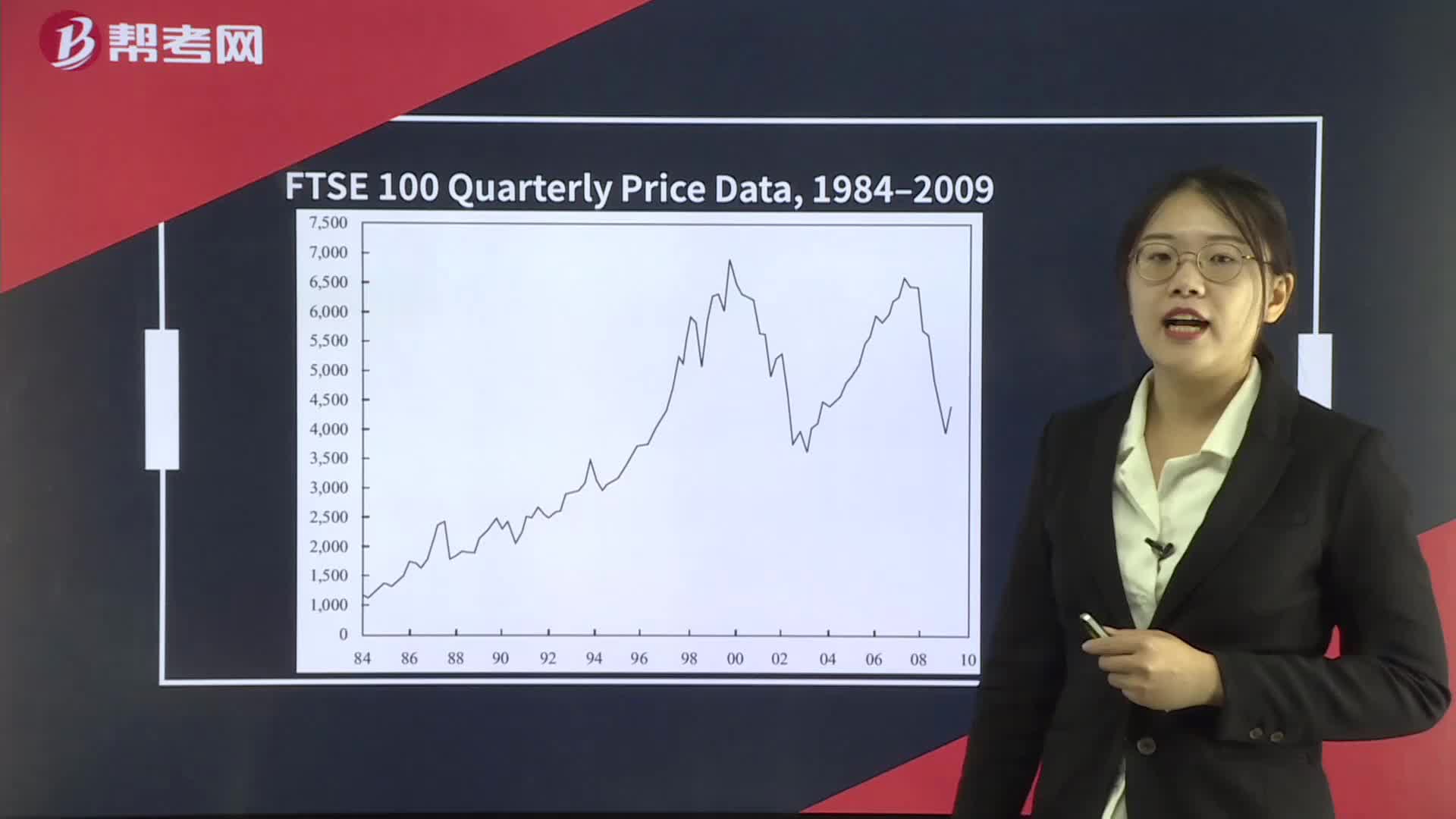
Technical Analysis Tools— Charts

Supply Analysis in Monopolistic Competition

Technical Analysis Tools— Chart Patterns

Intermarket analysis

Supply Analysis:The Firm
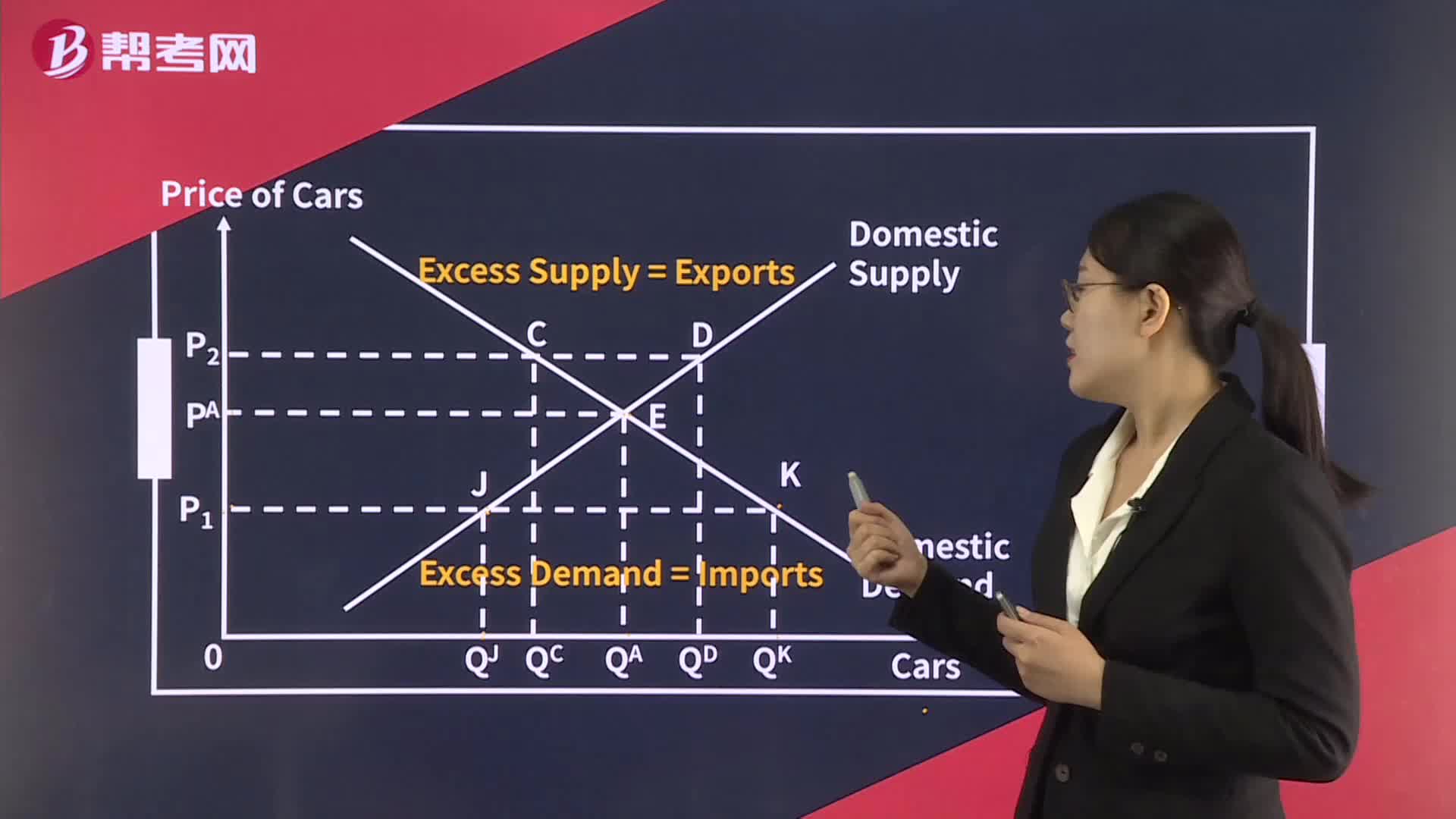
Excess Demand, Excess Supply

Natural Monopoly in a Regulated Pricing Environment

Monopoly

Breakeven Analysis

Supply Analysis:The Firm

Shifts in Aggregate Supply

下載億題庫APP
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360