Currency Regimes - Dollarization and Monetary Union

Currency Regimes - Currency Board System

Equilibrium GDP and Prices – Stagflation

Equilibrium GDP and Prices

The Relationship Between Fiscal and Monetary Policy
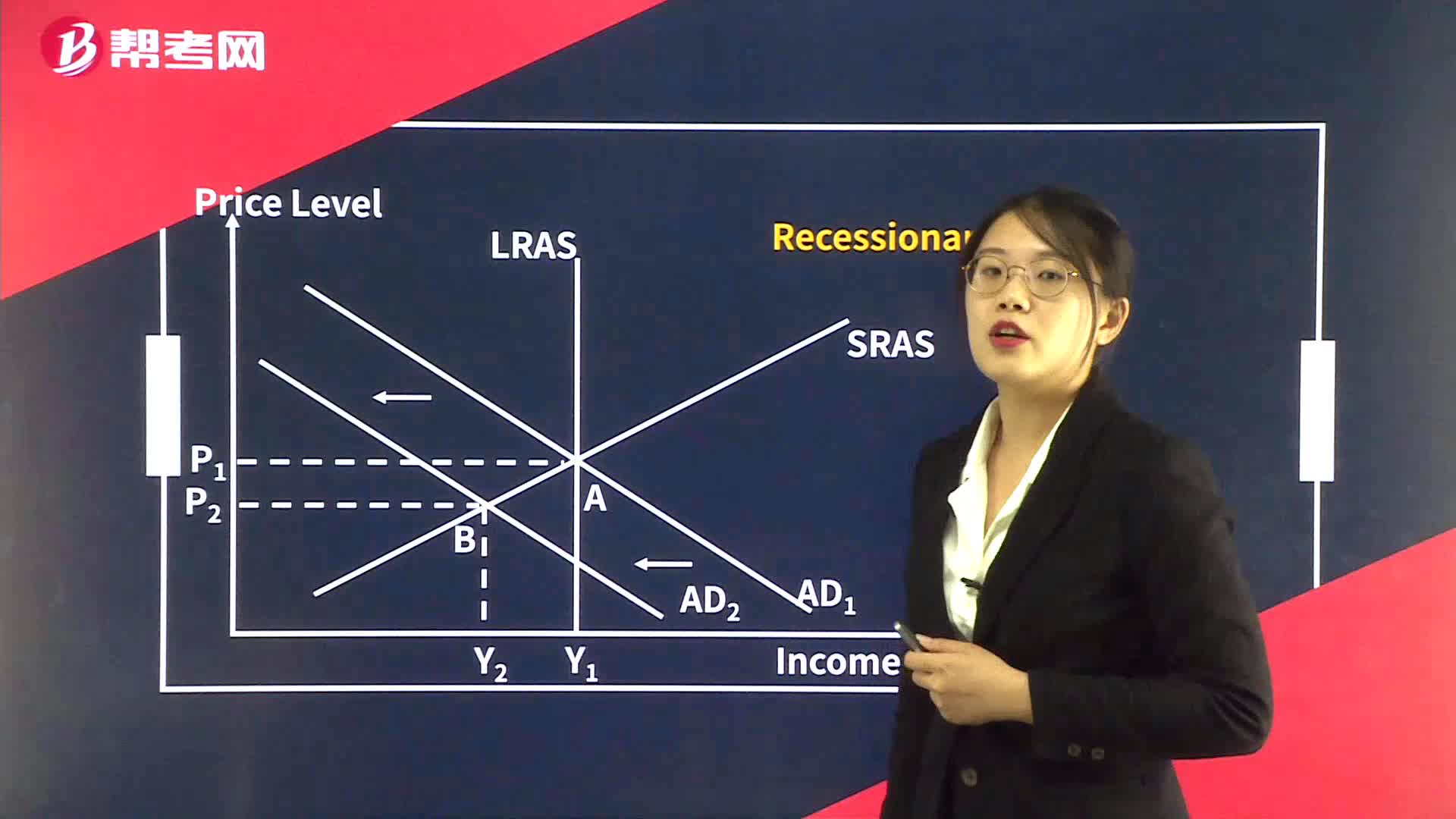
Equilibrium GDP and Prices - Recessionary Gap

Factors Influencing the Mix of Fiscal and Monetary Policy
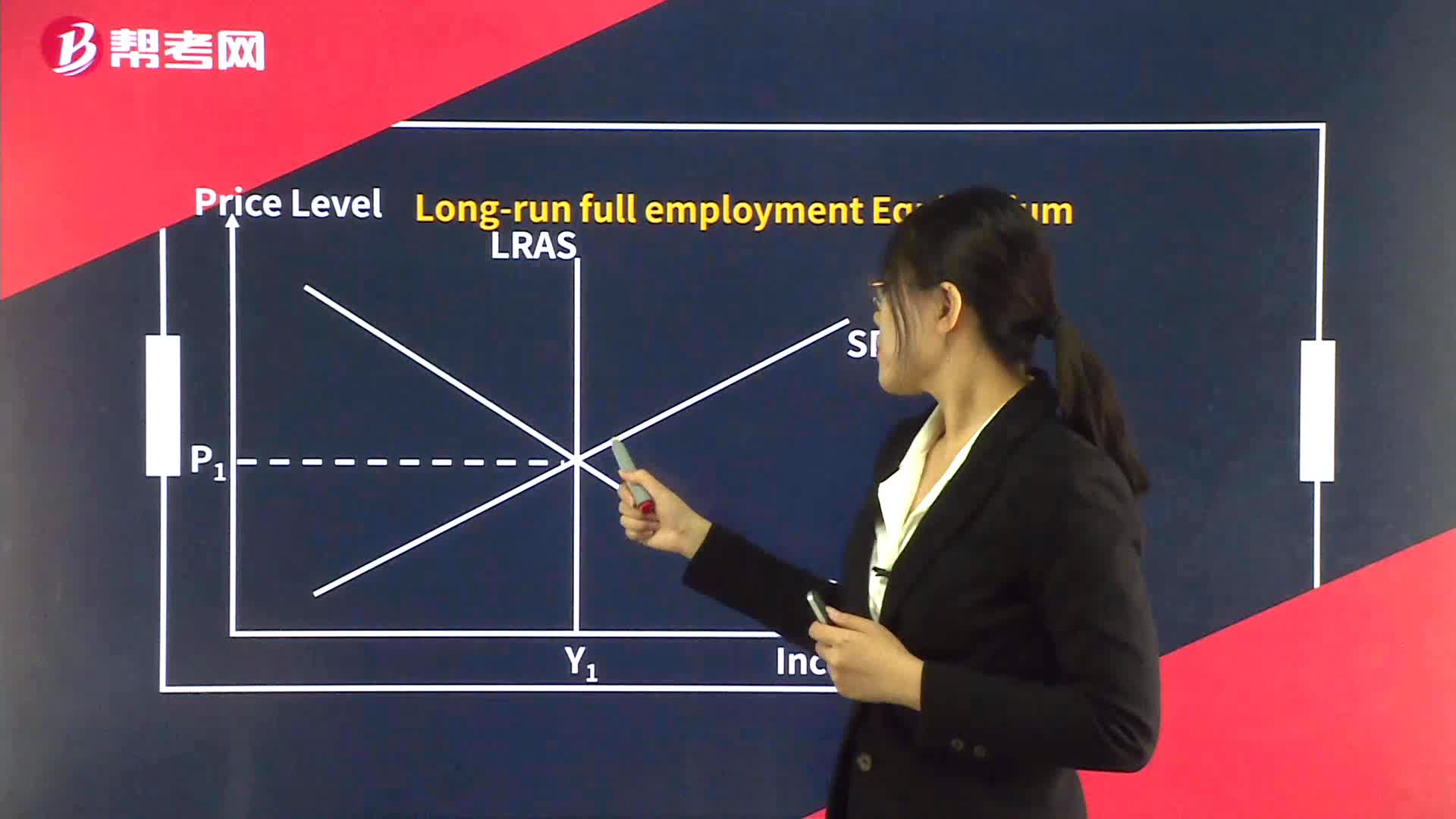
Equilibrium GDP and Prices - Long-Run Equilibrium

Price Indexes and Their Usage

Deficits and the Fiscal Stance

Overall Payroll Employment and Productivity Indicators
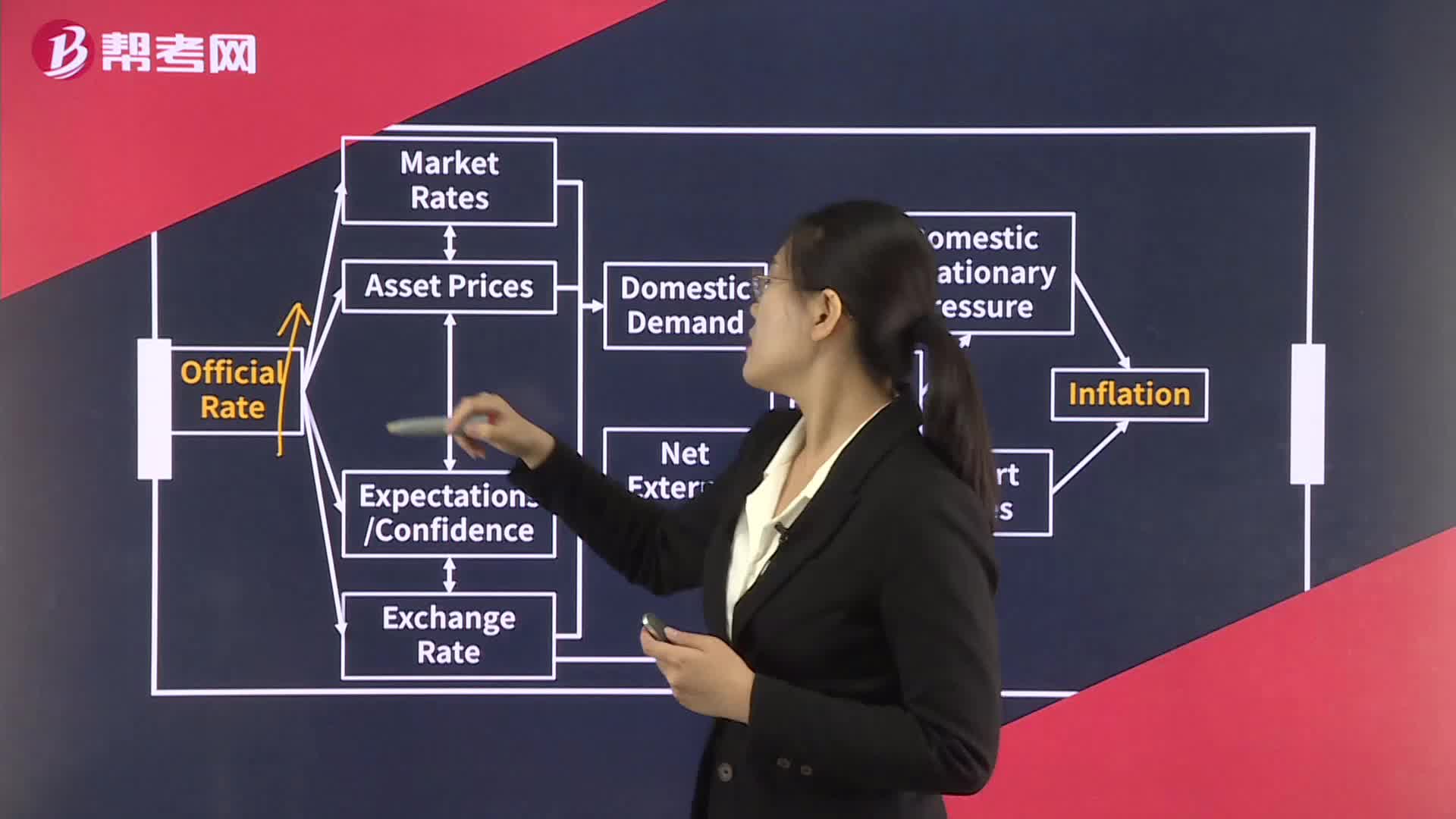
Monetary Transmission Mechanism

下載億題庫APP
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360