Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand

Distribution of the Sample Mean

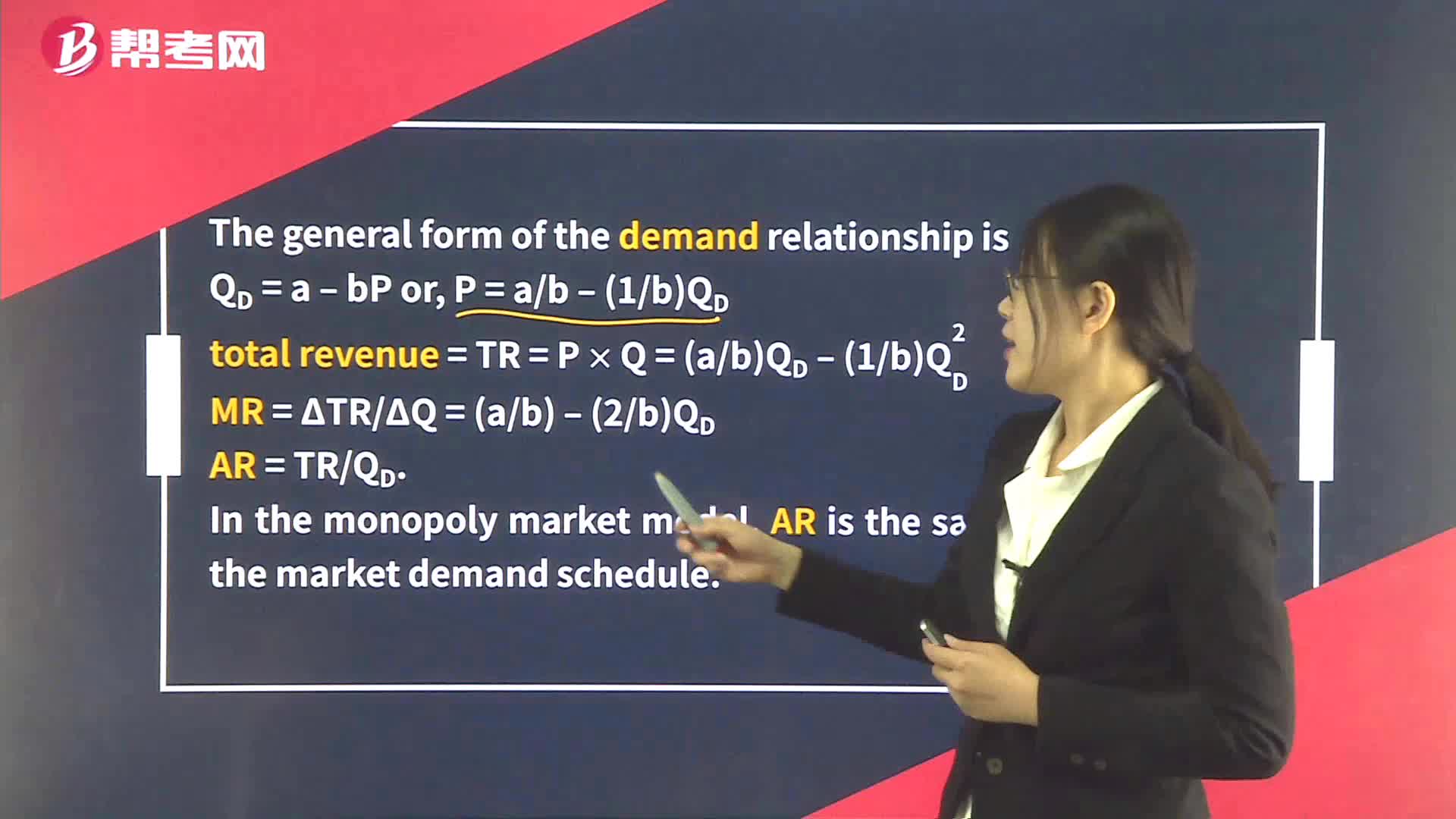
Demand Analysis:The Consumer

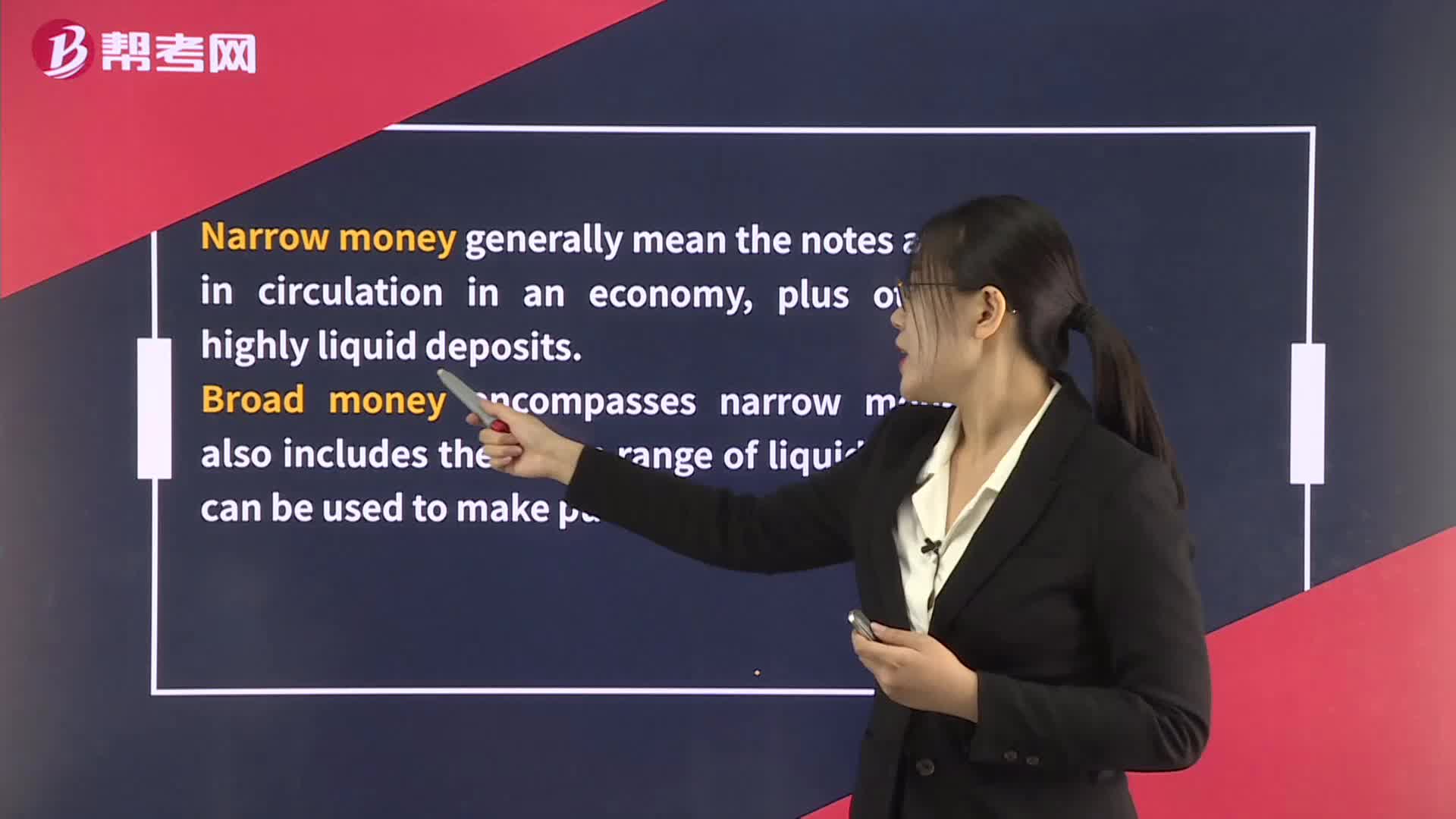
The Quantity Theory of Money
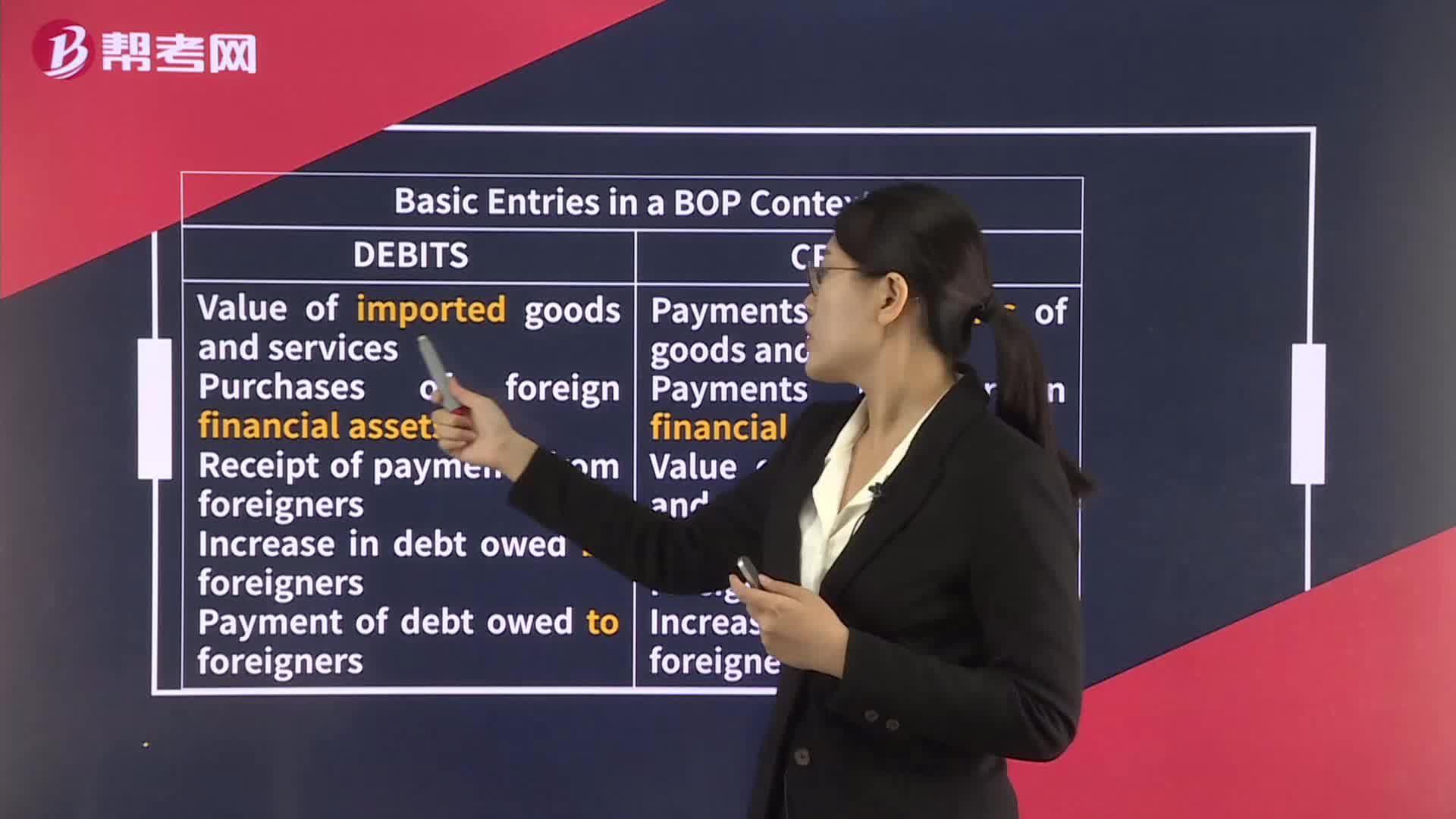
Balance of Payments Accounts

Balance of Payment Components

Kinked Demand Curve in Oligopoly Market

Shifts in Aggregate Demand
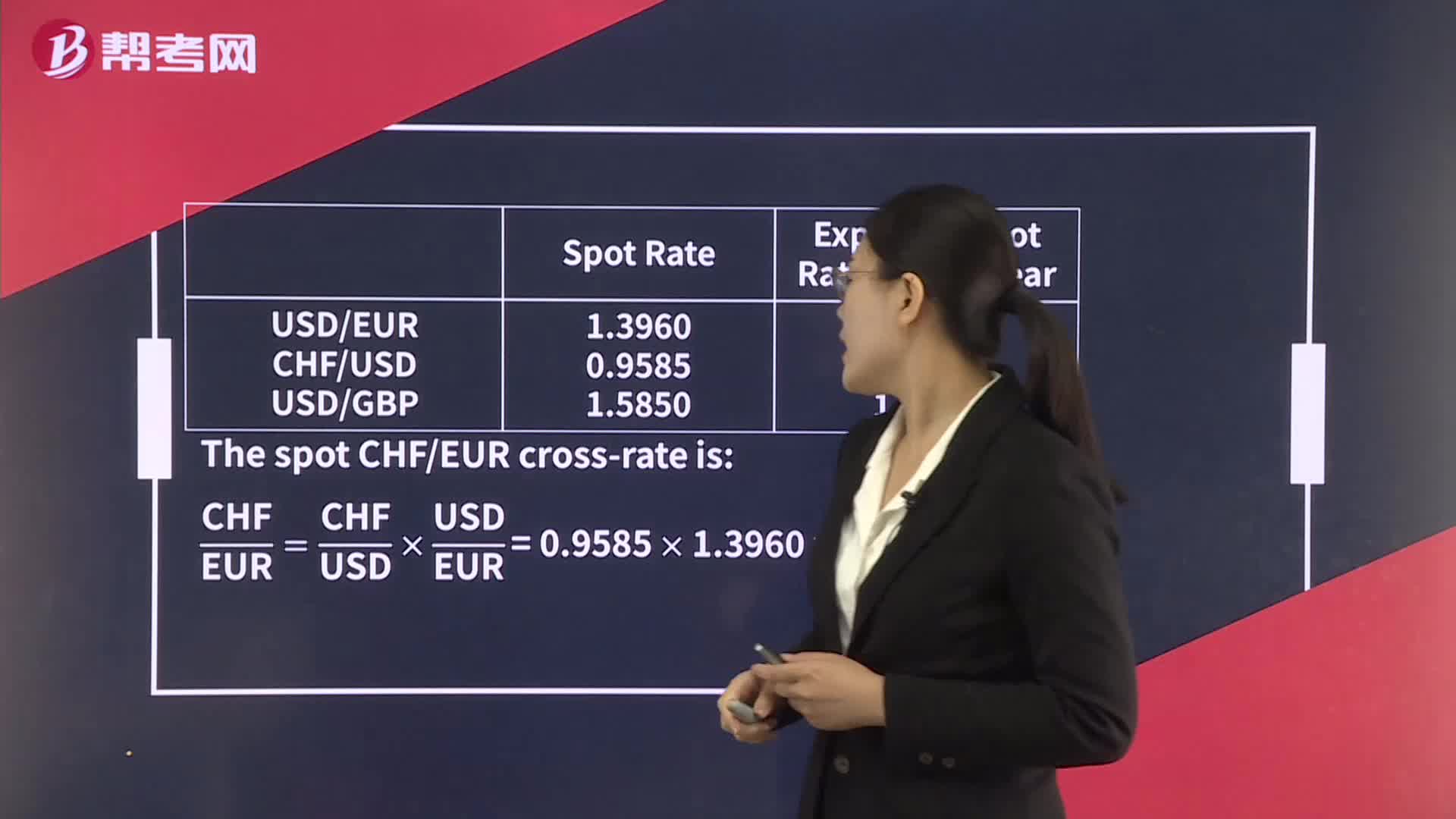
Cross-Rate Calculations

Shifts in Aggregate Demand and Supply

The Demand for Money

The Construction of Price Indexes

下載億題庫(kù)APP
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360